Understanding Bandwidth, Wavelength & Optical Windows in Fiber Optic Transmission
⭕ Understanding Bandwidth, Wavelength & Optical Windows in Fiber Optic Transmission
✅ Bandwidth:
Bandwidth refers to the capacity of a fiber optic cable to carry data signals. It’s like the width of a road, determining how much traffic (data) can flow through at once.
In fiber optic cables, bandwidth is typically measured in terms of frequency or data rate, representing the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over the cable within a given time period.
Higher bandwidth allows for greater data transmission rates, supporting applications that require high-speed communication, such as video streaming, cloud computing, and telecommunication networks.
✅ Wavelength:
Wavelength refers to the specific color of light used to transmit data through a fiber optic cable. It’s like the color of cars traveling on the road, each representing a different type of data.
Different wavelengths of light can be used simultaneously within a single fiber optic cable, allowing for multiple channels of communication (wavelength-division multiplexing or WDM).
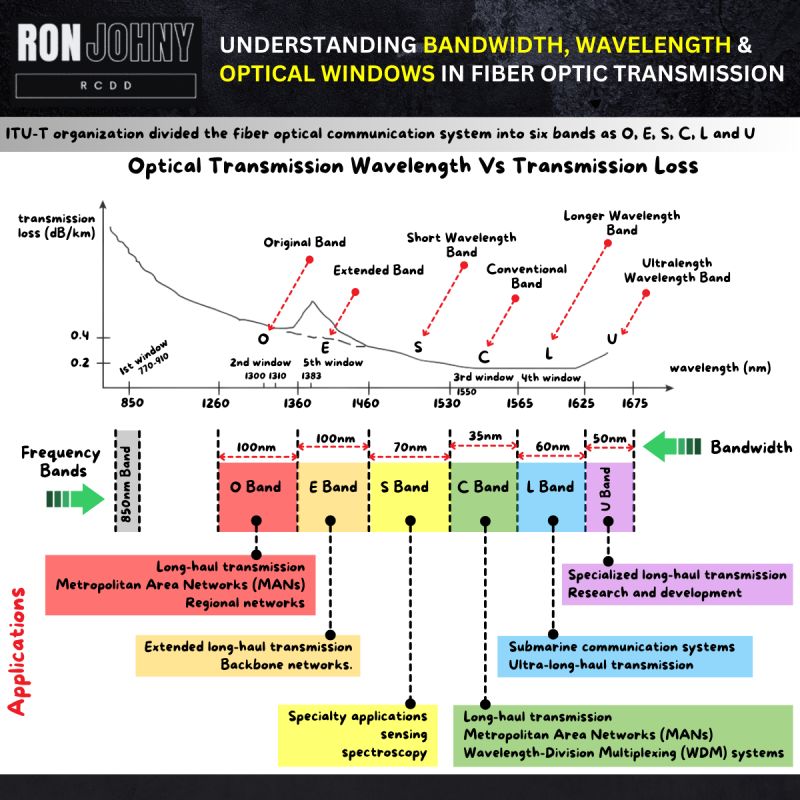
Commonly used wavelengths in fiber optic communication include 850 nm, 1310 nm, and 1550 nm, each with its own advantages and applications.
✅ Optical Window:
The optical window of a fiber optic cable refers to the range of wavelengths within which the cable exhibits low attenuation (signal loss) and dispersion (spreading of light pulses).
It’s like the clear section of a windshield through which you can see clearly while driving, ensuring that the transmitted signals remain strong and undistorted.
Fiber optic cables are designed to operate within specific optical windows, such as the 850 nm, 1310 nm, and 1550 nm windows, where signal loss is minimized, and data transmission is most efficient.
In summary, the bandwidth determines the capacity of the fiber optic cable to carry data, the wavelength determines the color of light used for transmission, and the optical window ensures efficient signal transmission by minimizing attenuation and dispersion within specific wavelength ranges.
Together, these factors play a crucial role in enabling high-speed and reliable communication through fiber optic cables.
Disclaimer – This post has only been shared for an educational and knowledge-sharing purpose related to Technologies. Information was obtained from the source above source. All rights and credits are reserved for the respective owner(s).
Keep learning and keep growing
Source: LinkedIn
Credits: Mr. Ron Michael Johny, RCDD








