How does an API work?
How does an API work?
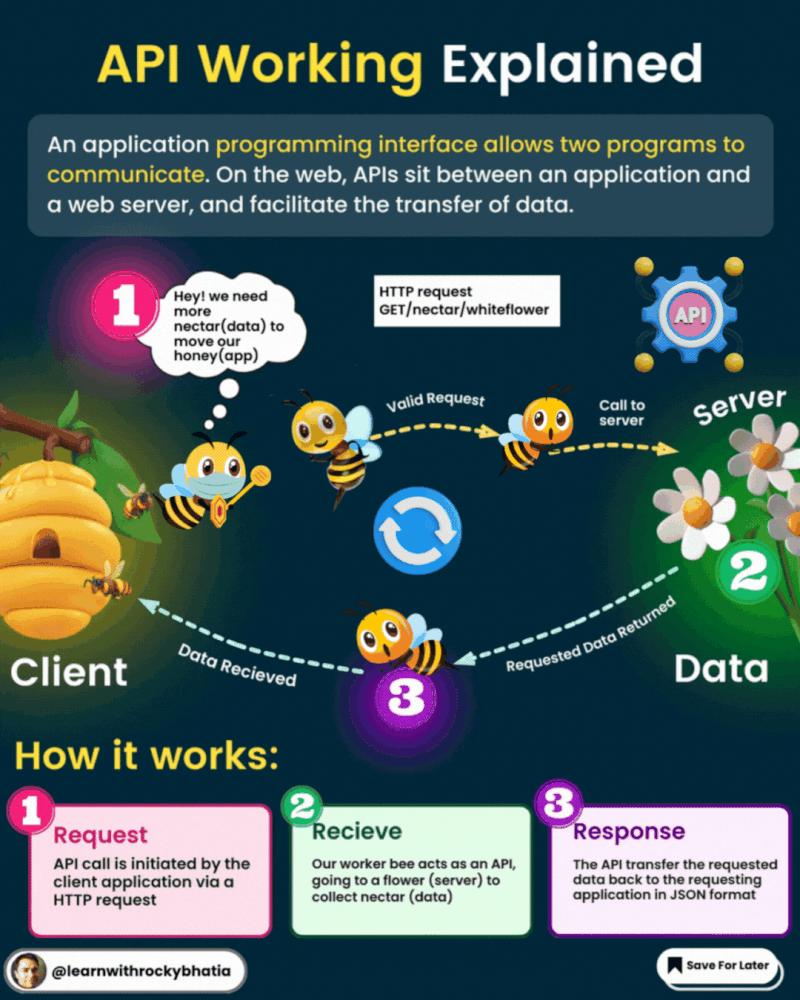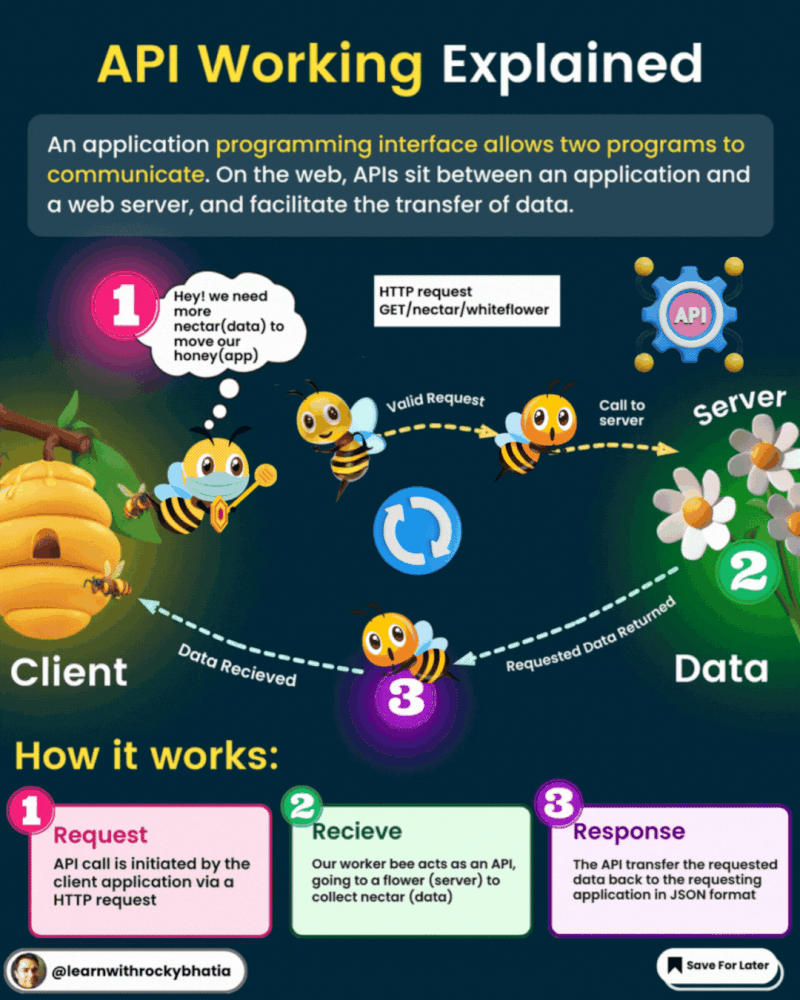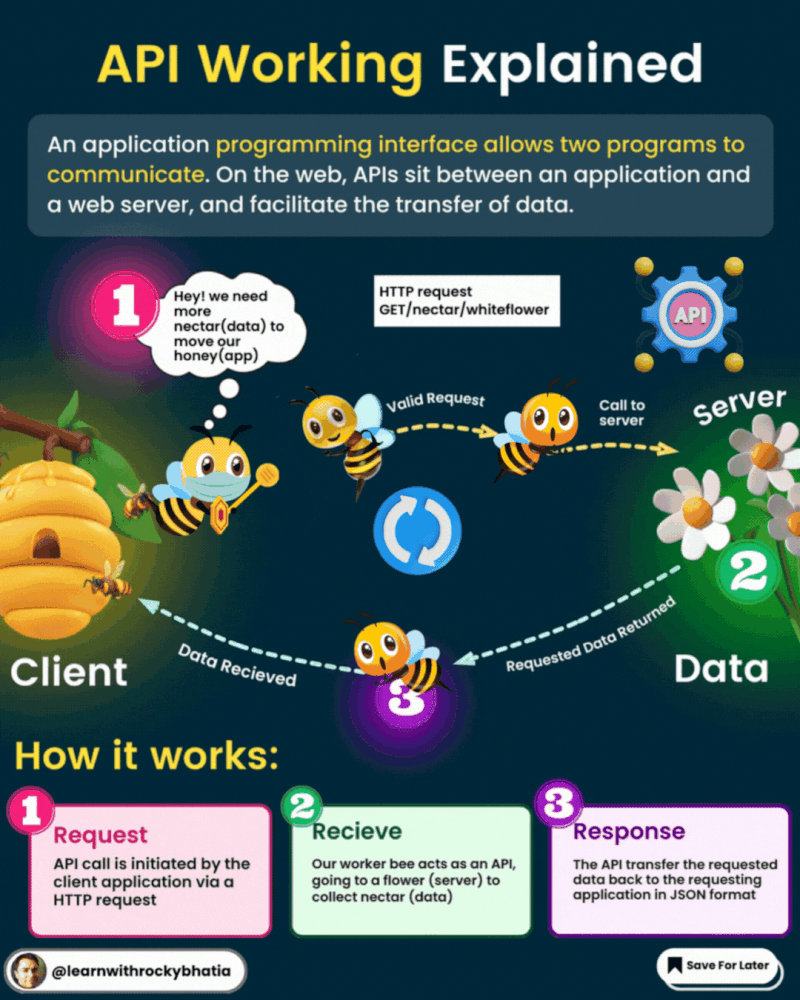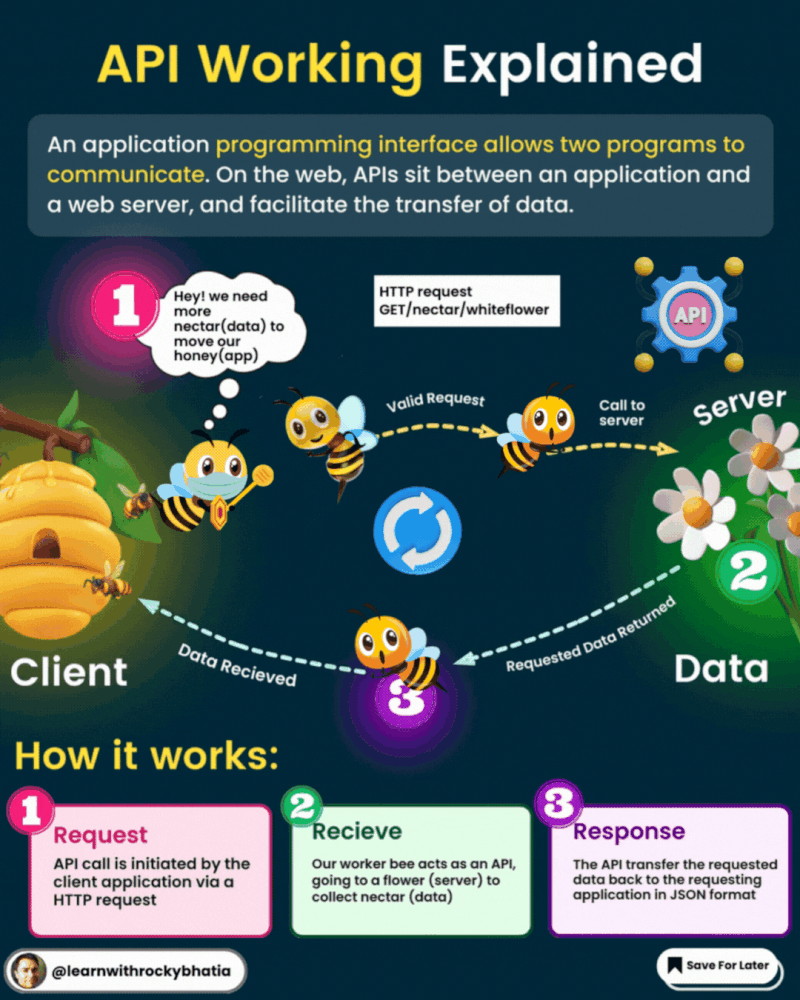
An API, or Application Programming Interface, acts as a bridge between software applications, enabling them to communicate and share data seamlessly. Here’s a quick breakdown of how APIs work:
1. Request: One software component sends a request to another component, often referred to as the client and server, respectively.
2. Communication Protocol: APIs follow predefined rules and conventions for communication, such as HTTP or HTTPS.
3. API Endpoint: The server provides specific URLs, known as endpoints, for accessing its services or data.
4. Request Parameters: Clients can send additional information along with their requests, like query parameters or request headers.
5. Processing: The server executes the requested operation, like fetching data from a database.
6. Response: After processing, the server sends back a response containing the requested data and an HTTP status code.
7. Data Format: Data exchanged between client and server is typically in standardized formats like JSON or XML.
8. Authentication and Authorization: APIs often require authentication to ensure security, using methods like API keys or tokens.
APIs play a crucial role in modern software development, facilitating communication and integration between various applications and services. From accessing external services to enhancing internal systems, APIs drive efficiency and collaboration in today’s tech landscape.
Image credit: Rocky Bhatia
Disclaimer – This post has only been shared for an educational and knowledge-sharing purpose related to Technologies. Information was obtained from the source above source. All rights and credits are reserved for the respective owner(s).
Keep learning and keep growing
Source: LinkedIn
Credits: Ms. Pooja Hooda








